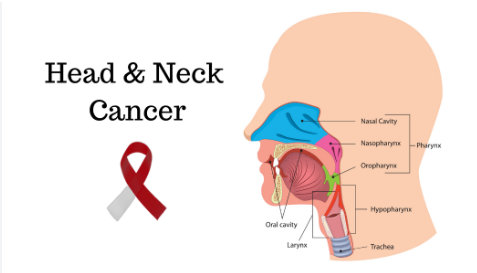
Head and neck cancers encompass a variety of malignancies that can affect areas such as the mouth, throat, voice box, sinuses, and nasal cavity. While these cancers can be aggressive, early detection and risk reduction strategies can significantly improve outcomes. Raising awareness about the risk factors, symptoms, and preventive measures is crucial in the fight against head and neck cancer.
Understanding Head and Neck Cancer
Head and neck cancers are a group of biologically similar cancers originating in the squamous cells that line the mucosal surfaces of the head and neck. These include cancers of the oral cavity, pharynx, larynx, nasal cavity, and paranasal sinuses. The most common type is squamous cell carcinoma, but other types can also occur.
Risk Factors
Several risk factors have been identified for head and neck cancers, many of which are preventable:
Tobacco Use: Smoking and smokeless tobacco are the most significant risk factors. They are responsible for approximately 85% of head and neck cancers.
Alcohol Consumption: Excessive alcohol use increases the risk, especially when combined with tobacco use.
Human Papillomavirus (HPV): Certain strains of HPV, particularly HPV-16, are linked to oropharyngeal cancers.
Sun Exposure: Prolonged exposure to the sun without protection can increase the risk of lip cancer.
Diet: A diet low in vitamins A and B can increase the risk, while a diet rich in fruits and vegetables can be protective.
Occupational Hazards: Exposure to wood dust, asbestos, and certain chemicals can increase the risk.
Genetics: Family history and genetic predispositions can also play a role.
Symptoms
Early detection is critical for successful treatment. Symptoms of head and neck cancer can vary depending on the specific location but generally include:
- Persistent sore throat
- Difficulty swallowing
- Hoarseness or changes in the voice
- Unexplained weight loss
- Ear pain
- Non-healing ulcers in the mouth or throat
- Lumps in the neck
Prevention and Risk Reduction
While not all cases of head and neck cancer can be prevented, several strategies can significantly reduce the risk:
Avoid Tobacco: Quitting smoking and avoiding smokeless tobacco is the most effective way to reduce risk. Support and cessation programs can help.
Limit Alcohol Consumption: Moderation in alcohol consumption can lower the risk.
Vaccination: HPV vaccination is recommended for preteens but can be administered up to age 26 (and sometimes beyond) to reduce the risk of HPV-related cancers.
Sun Protection: Use sunscreen and wear protective clothing to reduce the risk of lip cancer.
Healthy Diet: Consume a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and vitamins. Avoid processed and red meats.
Regular Dental Checkups: Regular visits to the dentist can help in the early detection of precancerous changes in the mouth.
Safe Work Practices: Use protective equipment and follow safety guidelines to minimise exposure to harmful substances at work.
Treatment Options
The treatment of head and neck cancer depends on the type, location, and stage of the cancer, as well as the patient’s overall health. Common treatments include:
Surgery: Removing the tumour and surrounding tissue.
Radiation Therapy: Using high-energy rays to destroy cancer cells.
Chemotherapy: Using drugs to kill cancer cells.
Targeted Therapy: Using drugs that target specific aspects of cancer cells.
Immunotherapy: Boosting the body’s immune system to fight cancer.
Importance of Awareness
Awareness campaigns play a vital role in educating the public about the risks and symptoms of head and neck cancers. Early detection through self-examination and regular medical checkups can lead to more effective treatment and better outcomes. Public health initiatives and educational programs are essential in disseminating information and encouraging healthy lifestyle choices.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What are the early signs of head and neck cancer?
Early signs often include persistent sore throat, difficulty swallowing, hoarseness, unexplained weight loss, ear pain, and non-healing mouth ulcers. It’s important to consult a healthcare provider if these symptoms persist.
2. How can I reduce my risk of developing head and neck cancer?
To reduce your risk, avoid tobacco and excessive alcohol use, get vaccinated against HPV, use sun protection, maintain a healthy diet rich in fruits and vegetables, and follow safety guidelines in occupational settings.
3. Is head and neck cancer treatable?
Yes, head and neck cancer is treatable, especially when detected early. Treatment options include surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy, depending on the cancer type, location, and stage.
Conclusion
Head and neck cancer is a serious health issue, but with increased awareness, early detection, and preventive measures, the risk can be significantly reduced. By making informed lifestyle choices and staying vigilant about symptoms, individuals can take proactive steps to protect themselves. Public health efforts and educational initiatives are key to spreading knowledge and encouraging behaviours that minimise risk and promote early detection, ultimately saving lives.